Deploying to AWS Lambda using the Serverless Application Model (SAM)
This guide illustrates how to deploy a Server-Side Swift workload on AWS using the AWS Serverless Application Model (SAM) toolkit. The workload is a REST API for tracking a To Do List. It deploys the API using Amazon API Gateway. The API methods store and retrieve data in a Amazon DynamoDB database using AWS Lambda functions.
Architecture
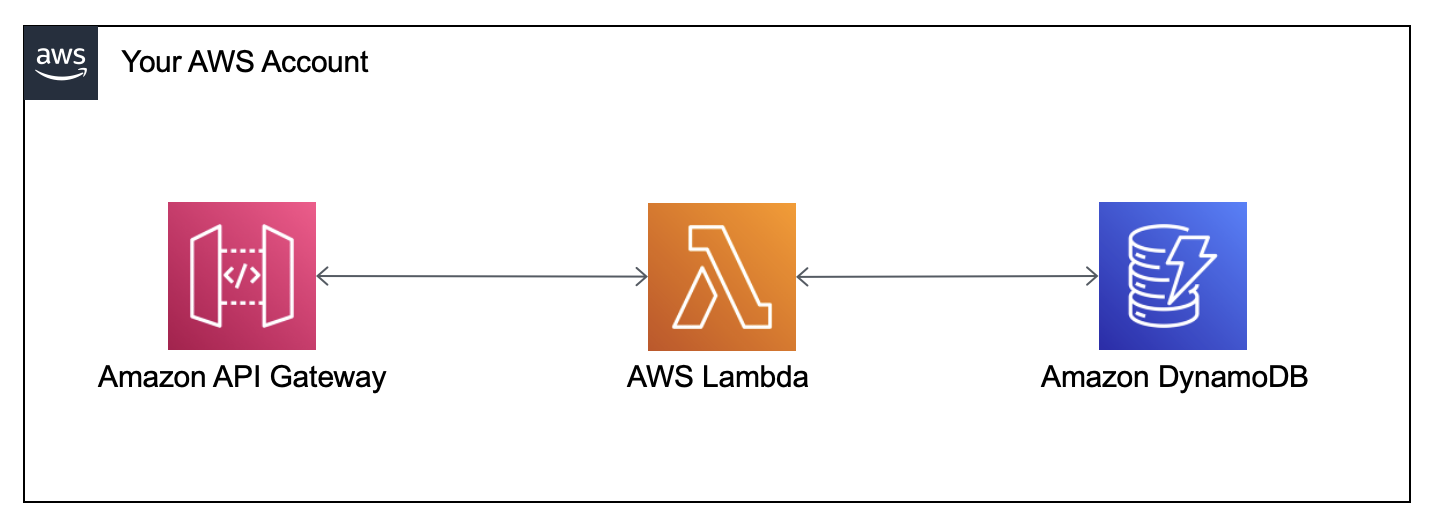
- Amazon API Gateway receives API requests
- API Gateway invokes Lambda functions to process PUT and GET events
- Lambda functions use the AWS SDK for Swift and the Swift AWS Lambda Runtime to retrieve and save items to the database
Prerequisites
To build this sample application, you need:
- AWS Account
- AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI) - install the CLI and configure it with credentials to your AWS account
- AWS SAM CLI - a command-line tool used to create serverless workloads on AWS
- Docker Desktop - to compile your Swift code into a Docker image
Step 1: Create a new SAM project
The SAM project creates resources (Lambda functions, API Gateway, and DynamoDB table) in your AWS account. You define the resources in a YAML template.
Create a folder for your project and a new template.yml file.
mkdir swift-lambda-api && cd swift-lambda-api
touch template.yml
Open the template.yml file and add the following code. Review the comments in the code to determine what it created in each section.
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09'
Transform: AWS::Serverless-2016-10-31
Resources:
# DynamoDB table to store your data
SwiftAPITable:
Type: AWS::Serverless::SimpleTable
Properties:
PrimaryKey:
Name: id
Type: String
# Lambda function to put items to the database
PutItemFunction:
Type: AWS::Serverless::Function
Properties:
# package the function as a Docker image
PackageType: Image
Policies:
# allow function to read and write to database table
- DynamoDBCrudPolicy:
TableName: !Ref SwiftAPITable
Environment:
# store database table name as an environment variable
Variables:
TABLE_NAME: !Ref SwiftAPITable
Events:
# handles the POST /item method of the REST API
Api:
Type: HttpApi
Properties:
Method: post
Path: /item
Metadata:
# location of the code and Docker file for function
DockerContext: ./src/put-item
Dockerfile: Dockerfile
DockerBuildArgs:
TARGET_NAME: put-item
# Lambda function to retrieve items from database
GetItemsFunction:
Type: AWS::Serverless::Function
Properties:
# package the function as a Docker image
PackageType: Image
Policies:
# allow function to read and write to database table
- DynamoDBCrudPolicy:
TableName: !Ref SwiftAPITable
Environment:
# store database table name as an environment variable
Variables:
TABLE_NAME: !Ref SwiftAPITable
Events:
# handles the GET /items method of the REST API
Api:
Type: HttpApi
Properties:
Method: get
Path: /items
Metadata:
# location of the code and Docker file for function
DockerContext: ./src/get-items
Dockerfile: Dockerfile
DockerBuildArgs:
TARGET_NAME: get-items
# print API endpoint and name of database table
Outputs:
SwiftAPIEndpoint:
Description: "API Gateway endpoint URL for your application"
Value: !Sub "https://${ServerlessHttpApi}.execute-api.${AWS::Region}.amazonaws.com"
SwiftAPITable:
Description: "DynamoDB Table Name"
Value: !Ref SwiftAPITable
Step 2: Initialize Lambda functions with SwiftPM
Lambda functions, written in Swift, process the API events. The PutItem function processes POST requests to add items to the database. The GetItems function processes GET requests to retrieve items from the database.
Use the Swift Package Manager to initialize a project for each function. You also add a Dockerfile to each folder.
mkdir -p src/put-item
cd src/put-item
swift package init --type executable
touch Dockerfile
cd ../..
mkdir -p src/get-items
cd src/get-items
swift package init --type executable
touch Dockerfile
Step 3: Update the Dockerfile
Docker is used to compile your Swift code and deploy the image to Lambda. Copy the following code into the Dockerfile you created in each function’s folder.
# image used to compile your Swift code
FROM --platform=linux/amd64 public.ecr.aws/docker/library/swift:5.7.2-amazonlinux2 as builder
ARG TARGET_NAME
RUN yum -y install git jq tar zip openssl-devel
WORKDIR /build-lambda
RUN mkdir -p /Sources/$TARGET_NAME/
RUN mkdir -p /Tests/$TARGET_NAME/
ADD /Sources/ ./Sources/
ADD /Tests/ ./Tests/
COPY Package.swift .
RUN cd /build-lambda && swift package clean && swift build --static-swift-stdlib -c release
# image deplpoyed to AWS Lambda with your compiled executable
FROM public.ecr.aws/lambda/provided:al2-x86_64
ARG TARGET_NAME
RUN mkdir -p /var/task/
RUN mkdir -p /var/runtime/
COPY --from=builder /build-lambda/.build/release/$TARGET_NAME /var/task/lambdaExec
RUN chmod 755 /var/task/lambdaExec
RUN ln -s /var/task/lambdaExec /var/runtime/bootstrap
RUN chmod 755 /var/runtime/bootstrap
WORKDIR /var/task
CMD ["/var/task/lambdaExec"]
Step 4: Update the Swift dependencies
Your project requires 3 libraries.
- swift-aws-lambda-runtime
- swift-aws-lambda-events
- aws-sdk-swift
You define these in the Package.swift file. Replace the contents of the Package.swift file in each function’s folder with the following code.
src/put-item/Sources/put-item/Package.swift
// swift-tools-version: 5.7
// The swift-tools-version declares the minimum version of Swift required to build this package.
import PackageDescription
let package = Package(
name: "put-item",
platforms: [.macOS(.v12)],
dependencies: [
.package(url: "https://github.com/swift-server/swift-aws-lambda-runtime", branch: "main"),
.package(url: "https://github.com/swift-server/swift-aws-lambda-events", branch: "main"),
.package(url: "https://github.com/awslabs/aws-sdk-swift", from: "0.9.1")
],
targets: [
.executableTarget(
name: "put-item",
dependencies: [
.product(name: "AWSLambdaRuntime",package: "swift-aws-lambda-runtime"),
.product(name: "AWSLambdaEvents", package: "swift-aws-lambda-events"),
.product(name: "AWSDynamoDB", package: "aws-sdk-swift")
]),
.testTarget(
name: "put-itemTests",
dependencies: ["put-item"]),
]
)
src/get-items/Sources/get-items/Package.swift
// swift-tools-version: 5.7
// The swift-tools-version declares the minimum version of Swift required to build this package.
import PackageDescription
let package = Package(
name: "get-items",
platforms: [.macOS(.v12)],
dependencies: [
.package(url: "https://github.com/swift-server/swift-aws-lambda-runtime", branch: "main"),
.package(url: "https://github.com/swift-server/swift-aws-lambda-events", branch: "main"),
.package(url: "https://github.com/awslabs/aws-sdk-swift", from: "0.9.1")
],
targets: [
.executableTarget(
name: "get-items",
dependencies: [
.product(name: "AWSLambdaRuntime",package: "swift-aws-lambda-runtime"),
.product(name: "AWSLambdaEvents", package: "swift-aws-lambda-events"),
.product(name: "AWSDynamoDB", package: "aws-sdk-swift")
]),
.testTarget(
name: "get-itemsTests",
dependencies: ["get-items"]),
]
)
Step 5: Update the Lambda function source code
Replace the contents of the main code file for each Swift project with the following code.
src/put-item/Sources/put-item/put_item.swift
// import the packages required by our function
import Foundation
import AWSLambdaRuntime
import AWSLambdaEvents
import AWSDynamoDB
// define Codable struct for function response
struct Item : Codable {
var id: String?
let itemName: String
}
enum FunctionError: Error {
case envError
}
@main
struct PutItemFunction: SimpleLambdaHandler {
// Lambda Function handler
func handle(_ event: APIGatewayV2Request, context: LambdaContext) async throws -> Item {
print("event received:\(event)")
// create a client to interact with DynamoDB
let client = try await DynamoDBClient()
// obtain DynamoDB table name from function's environment variables
guard let tableName = ProcessInfo.processInfo.environment["TABLE_NAME"] else {
throw FunctionError.envError
}
// decode data from APIGateway POST into a codable struct
var item = try JSONDecoder().decode(
Item.self,
from: event.body!.data(using: .utf8)!
)
// generate a unique id for the key of the item
item.id = UUID().uuidString
// use SDK to put the item into the database and return the item with key value
let input = PutItemInput(item: ["id": .s(item.id!), "itemName": .s(item.itemName)], tableName: tableName)
_ = try await client.putItem(input: input)
return item
}
}
src/get-items/Sources/get_items/get_items.swift
// import the packages required by our function
import Foundation
import AWSLambdaRuntime
import AWSLambdaEvents
import AWSDynamoDB
// define Codable struct for function response
struct Item : Codable {
var id: String = ""
var itemName: String = ""
}
enum FunctionError: Error {
case envError
}
@main
struct GetItemsFunction: SimpleLambdaHandler {
// Lambda Function handler
func handle(_ event: APIGatewayV2Request, context: LambdaContext) async throws -> [Item] {
print("event received:\(event)")
// create a client to interact with DynamoDB
let client = try await DynamoDBClient()
// obtain DynamoDB table name from function's environment variables
guard let tableName = ProcessInfo.processInfo.environment["TABLE_NAME"] else {
throw FunctionError.envError
}
// use SDK to retrieve items from table
let input = ScanInput(tableName: tableName)
let response = try await client.scan(input: input)
// return items in an array
return response.items!.map() {i in
var item = Item()
if case .s(let value) = i["id"] {
item.id = value
}
if case .s(let value) = i["itemName"] {
item.itemName = value
}
return item
}
}
}
Step 6: Build the SAM project
Building your SAM project uses Docker on your machine to compile your Swift code into Docker images. From the root folder of your project (swift-lambda-api) run the following command.
sam build
Step 7: Deploy the SAM project
Deploying your SAM project creates the Lambda functions, API Gateway, and DynamoDB database in your AWS account.
sam deploy --guided
Accept the default response to every prompt, except the following two:
PutItemFunction may not have authorization defined, Is this okay? [y/N]: y
GetItemsFunction may not have authorization defined, Is this okay? [y/N]: y
The project creates a publicly accessible API endpoint. These are warnings to inform you the API does not have authorization. If you are interested in adding authorization to the API, please refer to the SAM Documentation.
Step 8: Use your API
At the end of deployment, SAM displays the endpoint of your API Gateway:
Outputs
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Key SwiftAPIEndpoint
Description API Gateway endpoint URL for your application
Value https://[your-api-id].execute-api.[your-aws-region].amazonaws.com
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Use cURL or a tool such as Postman to interact with your API. Replace [your-api-endpoint] with the SwiftAPIEndpoint value from the deployment output.
Add a To Do List item
curl --request POST 'https://[your-api-endpoint]/item' --header 'Content-Type: application/json' --data-raw '{"itemName": "my todo item"}'
Retrieve To Do List items
curl https://[your-api-endpoint]/items
Cleanup
When finished with your application, use SAM to delete it from your AWS account. Answer Yes (y) to all prompts.
sam delete